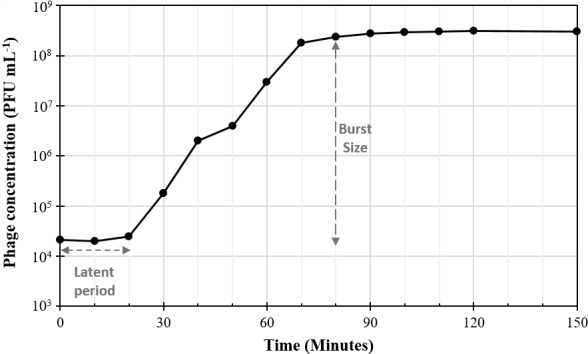
OBJECTIVETo isolate and characterize bacteriophage lytic for the opportunistic pathogen Klebsiella oxytoca and their formulation into a vary of solid dosage forms for in-vitro testing.RESULTSWe report the isolation, genomic and practical characterization of a novel bacteriophage lytic for Klebsiella oxytoca, which doesn’t infect the intently associated Klebsiella pneumoniae.
This bacteriophage was formulated into suppositories and troches and proven to be launched and lyse underlying Klebsiella oxytoca micro organism in an in-vitro mannequin. These bacteriophage formulations have been secure for at the very least 49 days at 4°C.
CONCLUSIONSThe profitable in-vitro assay of these formulations right here means that they might doubtlessly be examined in-vivo to find out whether or not such a therapeutic method may modulate the intestine microbiome, and management Klebsiella oxytoca overgrowth, throughout antibiotic remedy regimes.
CONCLUSIONSThis examine studies a novel bacteriophage particular for Klebsiella oxytoca which may be formulated into solid dosage forms applicable for potential supply in testing as a remedy to modulate intestine microbiome throughout antibiotic therapies.
The Xp10 Bacteriophage Protein P7 Inhibits Transcription by the Major and Major Variant Forms of the Host RNA Polymerase through a Common Mechanism.
The σ issue is a functionally compulsory subunit of the bacterial transcription equipment, the RNA polymerase. Bacteriophage-encoded small proteins that both modulate or inhibit the bacterial RNAP to permit the temporal regulation of bacteriophage gene expression usually goal the exercise of the most important bacterial σ issue, σ70. Previously, we confirmed that in Xanthomonas oryzae phage Xp10 an infection, the phage protein P7 inhibits the host RNAP by stopping the productive engagement with the promoter and concurrently displaces the σ70 issue from the RNAP.
In this examine, we show that P7 additionally inhibits the productive engagement of the bacterial RNAP containing the most important variant bacterial σ issue, σ54, with its cognate promoter. The outcomes counsel for the primary time that the most important variant kind of the host RNAP may also be focused by bacteriophage-encoded transcription regulatory proteins.
Since the most important and main variant σ issue interacting surfaces within the RNAP considerably overlap, however totally different areas of σ70 and σ54 are used for binding to the RNAP, our outcomes additional underscore the significance of the σ-RNAP interface in bacterial RNAP perform and regulation and doubtlessly for intervention by antibacterials.
